1. explain these sentences by giving examples.
* a specific are and the living and nonliving things found there form an ecosystem.
* there is a connection between all the living things occur in different areas.
* changes to an area affect the animals and plants that live there.
2.what effects can each of these human actions have on the environment?
*putting polluted water into the ocean
* creating protected natural areas
* building a new road
* out lawing the huntin of specific animals
3. how can we measure temperature by using a thermometer?what units is temperaturemeasured in?
basic content.
4.complete these sentences
* these elements influence the climate in an area: __________,_____________,_________and____________.
*temperature varies with_________and________
we measure temperature with a _______.
- there is more precipitation in _________,__________and__________.
- we use an anemometer to measure wind__________.we use a
_________to determinethe wind's direction.
5. copy and complete the table.
6. what are the main differences between these biomes?
* desert and tropical rain forest.
*decidous forest and chaparral.
7. match the numbers with the words. color the tropical zone red, the polar zones blue and the temperature zones orange.
equator artic circle
tropic of cancer tropical zone
tropic of capricorn temperate zones
antartic circle polar zones
8. copy and complete the diagram
The environment
All living things and the characteristics of the area where they live (temperature, humidity, soil etc…) from the environment.
A plant or animal can only survive in certain environment. Every living thing needs to live in a specific type of place. However people have adapted to beable to live anywhere.
Our environment is the whole planet
Environmental problems:
Environmental problems cause damage to the environment. They harm living things and their habitat.
The main environmental problems are:
1. Pollution: the accumulation of harmful substances on the ground, in the air and in the water causes pollution. These substances harm living things.
2. Deforestation: is the disappearance of forests. Cutting down too many trees, pollution and fires all cause deforestation.
3. Desertification: is the transformation of some landscapes into desert areas. The soil becomes very dry and poor. Few living things can survive in these areas.
4. Habitat loss: occurs when natural areas are destroyed to make room for housing or industry. Habitat loss can also occur because of deforestation or desertification.
5. Excessive development, hunting, fires and other actions can use the extinction of living things.
Solutions
1. Reduce pollution.
2. Avoid cutting down wild trees for wood.
3. Outlaw the hunting of animals.
4. Protect specific natural areas.
Class work
Explain these sentences by giving examples:
• A specific area ecosystem.
• There is a connection between all the living things in an ecosystem.
• Different living things occur in different areas.
• Changes to an area affect the animals and plants that live there.
What effects can each of these human actions have on the environment?
• and the living and nonliving things found there from and
• Putting polluted water into the ocean.
• Creating protected natural areas.
• Building a new road.
• Outlawing the hunting of specific animals
Development
Because in the ecosystem if there are living beings and nonliving creatures. for example: plants, animals, stones and more.
I think because there is nothing if not living in an ecosystem.If clear affects animals and living things because their habitat is no longer the same.
if for the living and the things we have not even found in many different areas.
if animals are used unclear why living in a very different climate
if we place in the sea water contaminated animals may die because the previous water was not polluted.
Biomes
Is a group of ecosystems that have similar light, temperature, humidity and living things?
For example: the rain forest in the world.
Specific living things occur in each type of biome. Each biome is in a specific climatic zone.
Biome of warm zones:
There are three types of biomes in warm zones:
The desert: is a biome where there is a little water. The temperatures are very high during the day and very low at night. Cacti, coyotes and camels live in the desert biome.
Tropical rain forest: it rains a lot. It is very humid and warm, are also very dense, they have a lot of trees, like rubber trees, and animals like the toucan.
The savanna: is a biome where a very dry season is followed by rainy season every year.
The most common plants are types of grass. The trees grass for apart from each other.
Giraffes and lions live in the African savanna.
Temperate zone biomes: this biomes are in the temperate zones.
Chaparral: evergreen plants and brushes are found here. These plants can survive hot, dry summers. Typical plants include thyme and oak. Rabbits and boars live here.
Temperate forest: pine trees and trees that lose their leaves in autumn are typical of these forest. Spruce and elm trees, deer and bears live here.
Prairies and steppes: this biome is a large plain covered with grass. There are few trees the prairie dog and the bison live in this biome.
Biomes of cold zones: the tundra and boreal forest are in cold zones.
The tundra: Has very low temperatures. Lichens and small plants like moss are characteristic plants. Reindeer and the arctic fox live here.
Boreal forest: are cold zone forest characteristic plants include lichens, pine trees and fir trees. The ground of boreal forests is covered with ice and snow for many months of the year. The beaver and the Canada lynx live in this biome. Boreal forests are also called taiga.
Factors involved in climate
The climate of on area several factors, these factors change from one place to another. They depend on how far a place is from equator, how far it is from the ocean and its altitude.
Temperature: varies with distance from the equator and altitude. At high altitudes, the temperature is lower. At low altitudes, temperature is higher. Temperatures are milder on the coasts than in inland regions. This is due to the influence of the ocean.
Precipitation: such as rain, snow and hail, comes from the water in the atmosphere. There is more precipitation near the equator, on the coast and in the mountains. We use a rain gauge to measure precipitation.
Pressure: is the force s on that air exerts on the earth’s surface. Pressure varies with altitude. High areas have low pressure. Low areas have high pressure. We use a barometer to measure pressure.
Wind: is the movement of air. Winds move between areas that have different temperatures and pressures. We use an anemometer to measure wind speed. We use a weather vane to determine its direction.
Climatic zones: we can divide the earth into large climatic zones depending on the type of climate in each zone:
Tropical zone: is located between the tropic of cancer and the tropic of Capricorn. The temperatures are very high because the sun’s rays are perpendicular to the earth’s surface.
Polar zones: there are two; one is in the northern hemisphere, north of the Artic circle. The other is in the southern hemisphere, south of the Antarctic Circle. The temperatures at the poles a very low because the sun’s rays are very slanted when they reach the earth.
Temperate zones: there are two, on each hemisphere. They extend from the tropics to the polar circles. The temperatures in these areas are not extreme. This is because the sun’s rays are slightly slanted when they reach the earth.
The distribution of these zones generally depends on their distance from the equator. Within each zone, distance from the ocean and altitude also cause climatic differences.
Solar energy
The sun, a source of energy.
Earth does not emit its own light. It comes from the sun. The sun is constantly producing energy. This energy travels through space and reaches earth as heat and light.
Heat: it travels to earth by means o radiation. The sun’s rays reach different places on earth at different angles, that’s why there are hotter and colder areas.
Perpendicular rays= hotter diagonally rays= colder
Light: is a form of energy. The light that comes from the sun looks white, but is made up of many colors.
Light propagates in straight line and all directions, light travels at great speed.
Some objects allow light to pass through them, transparent.
Some objects do not let light pass through them opaque.
Some objects only let part of the light pass through them translucent.
Reflection: it’s when light changes direction when it hits and objects.
Refraction: it’s when light changes direction when it passes from one substance to another.
Earth is a magnet
· Magnets: are objects that attract iron and steel. This force of attraction is called magnetism.
· Electromagnets: are artificial magnets. They need an electric current to work.
Earth’s magnetic field
Earth is a giant magnet. Like all magnets, it has two magnetic poles:
· Earth’s magnetic south pole is in northern Canada
· Earth’s magnetic north pole is near the Antarctic coast.
Matter and energy on earth
Mater changes:
Earth, like all other things, is made of matter. It has a lot of a mass and large volume.
Matter is made of many different substances (salt, water, wood etc…) these substances may be mixed together.
For example: seawater contains many salts.
Earth’s matter exists in three states:
Solid, like rocks
Gaseous, like air
Liquid, like water
Matter is constantly changing, these changes can be:
· Physical changes: some examples of physical changes of state, movement and fragmentation.
Changes of state are constantly occurring. For example, liquid lava comes out of volcanoes and becomes solid when it reaches the surface.
Earth is constantly moving. It rotates on its axis (rotation) and it orbits the sun (revolution). The matter on earth is also moving. Examples of movement of earth’s matter are:
· Tornadoes
· Oceans
· Water currents
· waterfalls
the movements of air and water break up water.
For example, the movement of waves breaks up rocks, and wind erodes soft rocks like limestone.
The external forces of earth.
Wind, water and people erode the relief of earth surface.
These changes occur slowly, over millions of years.
External changes happen in three phases:
1. Erosion: is the constant wearing away of rocks and soil.
Temperature, water, wind and people cause erosion.
· Sharp changes in the temperature: break rocks into fragments. This occurs in areas where there is a big difference between daytime and nighttime temperatures, such as mountains and deserts. Sometimes water that has filtered through cracks in rocks freezes. This act like a wedge and breaks the rock.
· Rainwater, rivers and oceans: constantly erode the ground.
Rain and snow dissolve the materials in the soil. Rivers wear away banks and erode materials from the rivers bed.
They create deep valleys and canyons. The waves of the ocean wear away the coasts. Underground water hollows out large caves.
· The wind: mostly erodes soft rocks. It also erodes places where there is a lot of sand, like deserts and beaches.
· The people: cut down forests. They cause fires, build slopes, etc. this actions cause erosion of the soil.
2. Transporting materials: eroded materials are transported from one place to another. The wind, river currents and ocean water transport these materials. Wind curries sand and small rocks. Rivers and oceans carry large amounts of dissolved materials. They also carry larger materials floating on the surface.
3. Sedimentation: occurs when the materials carried by water, ice or wind are deposited. The accumulation of these materials leads to changes in the lanscape.
· A river transports the materials. It deposits them on its banks to create terraces. It deposits at is mouth to create deltas.
· Ocean waves deposit materials on the low shores. The deposited materials create beaches.
· The wind transports large quantities of sand. This creates dunes in deserts and on the coast
}
The internal forces of Earth
Earth changes: the relief of earth’s surface has not always been the same.
For example:
Islands and mountains have formed throughout time. Millions of years ago, there were plains where today there are mountains, and vice versa. Land now on the surface used to be under the ocean.
These changes occur as a result of the internal and external forces of earth.
Internal forces: create the surface relief.
External forces: erode the surface little by little.
Earthquakes: occur when internal forces break or move rocks inside earth. The rocks knock against each other and cause very intense and destructive seismic waves.
Earthquakes begin inside earth at a point called focus.
This point is called the epicenter on the surface.
The size or force of an earthquake is measured by a sale called richer scale and goes from 1 to about 9. The most intense earthquakes can change the lanscape.
Volcanic eruptions:
There are very hot substances inside earth. Sometimes these substances break through to the surface. They come out through to the surface. They come out through volcanoes.
The hot materials form magma. Internal forces put pressure on the magna and it rises through the central vert and comes out of the crater.
The substances that the volcano expels can be solid, like ash. They can also be liquid like lava. Volcanoes can also expel gases, which can cause explosions inside the volcano.
These expelled substances build up on the outside of the volcano and form volcanic cones. Sometimes volcanic eruptions can even create islands, such as the Hawaiian Islands.
Features of earth
Shape and size of earth:
Earth is spherical. The other planets in the solar system are also spherical. But earth is not a perfect sphere. It is flattened at the poles. We call this shape a GEODE.
The surface of earth:
We can see different colors on the surface of earth if we look at it from space. These correspond to there different areas.
*some areas are solid land. These areas are called the “LITHOSPERE”.
Part of the lithosphere is under the oceans.
Other part is above the oceans and some the continents and islands.
There are seven continents
Africa
Asia
Europe
North America
South America
Australia/Oceania
Antarctic
The continents and islands cover a quarter of earth’s surface.
*other areas are covered by water. This is called the “HYDROSPHERE” it includes oceans, seas, rivers, lakes and ice
There are five oceans:
The pacific
The Atlantic
Indian
Artic
Antarctic
The hydrosphere covers three quarters of earth’s surface.
*A large layer of gases surround earths. These gases make up the “atmosphere” nitrogen and oxygen are the main gases in the atmosphere. Meteorological phenomena occur in the lowest part of the atmosphere.
For example: changes in the temperature and storms occur here.
Higher up is ozone layer. This layer stops some of the sun’s rays from reaching earth life on the planet would be impossible if these rays reached earth.
The interior of earth
Earth has three layers:
*the crust: is the surface layer of earth. It is made up of solid material. It is thicker in areas where there are large mountain chains like the Andes.
It is thinner under the oceans.
*the mantle: is the intermediate layer of earth. It is divided into two parts:
-the upper mantle: is made up of solid rock.
-the lower mantle: is partly made up of molten rock.
*the core: is the deepest layer of earth. It is basically made of iron. It is very hot. Some parts of the core are liquid.
Continental crust is thicker and less dense and oceanic crust is thinner and more dense.
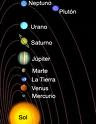
The solar system
The sun and all the celestial bodies that orbit it from the solar system. The solar system contains nine planets and their satellites.
Our solar system is part of the Milky Way galaxy.
The sun:
The sun is a star; it gives off heat and light. It appears yellow and is made up of gases. The sun is very big. It is bigger than all the planets in the solar system put together. It is more than a million times bigger than earth.
However, the sun is not particularly large for a star. It looks bigger than other stars because it is nearer to earth.
Earth receives heat and light from the sun. Earth is exactly the right distance from the sun for life to be possible here. If earth were nearer to the sun, the heat would burn us. If earth were father away, the cold would make life here impossible.
Planets and satellites:
Nine planets revolve around the sun. The path these planets take around the sun is called their orbit.
Planets:
*mercury: is much smaller than earth. Mercury has the shortest orbit around the sun
*Venus: is similar in size to earth, it is the brightest planet. Its surface has the highest temperatures.
Earth: is the only planet in the solar system to here there is life.
Mars: is an intense red color, it is full of craters and volcanoes. Some of these volcanoes are bigger than any mountain on earth
Jupiter: is the biggest planet I the solar system. T has a red pot on its surface.
Saturn: is surrounded by thousands of rings are made up of millions of small particles.
Uranus: Have characteristics blue-green color.
Neptune: is one on farthest planets from the sun, it is blue
Pluto: is the smallest planet. It is the farthest planet from the sun which is why it is also the coldest planet.
All the planets in the solar system except mercury and Venus have satellites the moo is earth’s only satellite.
The movements of earth
Earth’s constantly moving like all the planets in the solar system earth orbits the sun. It also rotates constantly.
-rotation: earth rotates on a imaginary axis.This axis crosses earth from the north pole to the south pole.
earth take 24 hours to make rotation.This are the 24 hours in a day. rotation produces the sequence of day and night.
revolution: earth also orbits the sun. earth takes about 365 days to complete one revolution around the sun.these are the 365 in a year.every fourth years has an extra day. these are leap years
The earth and the universe
The universe: all the bodies sky between the spaces them form the universe. The universe is very old. It began 15 bition years ago after a large explosion distances are huge in the universe.
For example:
The light emitted by the star nearest our solar system takes for years to reach our planet.
Celestial bodies:
There are many different bodies in the sky. These incluse stars, light the sun, planet, light, earth, and satellites, light the moon they are old called celestial bodies. They are two types of celestial bodies. Stars all luminous celestial bodies this means.
-they emit their own light
-they look likes small pants of lights.
-they are infact very big. Stars are different colors:
The hottest are blue and coolest are yellow and red.
*nonluminous celestial bodies
Planets, satellites, and comets are nonluminous celestial bodies this means they to not emit their own light.
-planets: orbit start
-satellites: orbit planets
-the Lune: is the earth’s only satellite
-comets: comets are small celestial bodies that orbit the sun. They do not emit their own light. They are made of ice and dust; these materials became luminous in the atmosphere and form a long tail. Comets are visible from earth periodically.For example: the hale Bopp comet can be seen every to thousand 2,364 years.ConstellationsWhen we look up at the stars from earth, they are appear to be in groups of stars are cold constellations.GalaxiesCelestial bodies are not isolated. They form groups’ cold galaxies. There are many millions of galaxies in the universe. Each galaxy is made up of millions of celestial bodies. Earth is in the Milky Way galaxy. Galaxies have different shapes.
Hormones are substances that control very important process in the human body. For example, hormones are involved in growth, puberty, and breast-feeding. Hormones are produced in organs called endocrine organs. The hormones enter the bloodstream and reach other organs, where the have a specific effect.
The pituitary gland is an endocrine organ it is located in the brain. The thyroid is also an endocrine organ. it is located inside the neck, in front of the larynx.
If the spectrum of a star is studied with high-resolution methods can be seen many dark lines at certain wavelengths. These lines are due to light absorption in the deeper layers of atoms of the upper, cooler. The atoms in the star are identified by comparing the stellar absorption lines with those produced in the laboratory by gas known; you can also calculate the temperature and pressure of the atmosphere and the relative abundance of chemical elements. See Fraunhofer lines. Most of the stars are at a stage of its life known as the "main sequence", at this stage, the temperature and luminosity increase with mass. Some stars are brighter and therefore larger than the sequence of the same temperature: the so-called red giant stars. Many stars are weaker and therefore smaller than the sequence of the same temperature, such as white dwarfs (1% of the diameter of the Sun) and neutron stars (0.001% of the diameter of the Sun). Theoretical models of stellar interiors have been calculated based on the theory of balance between the force of gravity, contributing to the collapse of the star, and the pressure of reheated gas, which tend to expand. High temperatures also drive a stellar heat flow from inside to outside the star. For the star is in equilibrium, this heat loss must be offset by the energy released in nuclear reactions internal. As above the various nuclear fuels, the star evolves slowly, and the core shrinks to increasing densities.
The nervous system
Enables us to:
- What happens around us.
-respond to what happens, such as by making movements.
-coordinates all the organs and systems in the human body.
-the brain spinal cord and nerves form it.
The brain:
It is in the head, it’s protected by the bones of the skull.
a. The cerebrum: is the biggest structure of the brain, it controls all the voluntary actions.
Example:
- Riding a bicycle.
- Speaking.
- Eating.
The cerebrum also stores data and memories; it is involved in how it we feel, like when we are afraid or happy.
It also interprets information gathered by the sense organs.
b. Cerebellum: is collocated below the cerebrum. It coordinates movements and controls balance.
c. Brain steam: connects the brain with the spinal cord. The brain steam controls many process in the human body.
Example:
Controls heartbeats.
Movements we make when we breathe.
The spinal cord: is in the back, it goes from the top of the back bottom. It is protected by the vertebrae of the spinal column. The spinal cord is shaped like a cylinder.
-many nerves branch from the spinal cord.
-they go to the organs in the torso.
*stomach.
*limbs like the biceps.
- The spinal cord controls involuntary movements called reflexes.
Nerves:
-are shapes long fibers.
-they connect the brain and the spinal cord with the rest of the organs in the body.
-there are two types of nerves.
A. sensory nerves: carry information from the organs to the cerebrum and the spinal cord.
Example:
The auditory nerve carries information about sounds from the ear to the cerebrum.
B. motor nerves:
Carry information from the brain and the spinal cord to other organs. Motor nerves tell the body to make movements.
Example:
There are nerves that go from the spinal cord to the quadriceps muscle in the leg these nerves send the muscle an order to move so that you can walk.
Nerves coordinate all the functions of the body.
The skeletal – muscular system:
It is responsible for body movements. The skeleton and muscular systems form the skeletal – muscular system.
The skeleton:
All the bones in the human body form the skeleton; the skeleton has three important functions:
1. It sapports and gives shape to the body.
2. It protects the internal organs.
3. It provides a base for muscles. When muscles pull on the bones they are attached to, the bones move. That is how you can’t lift a arm, walk or make any other movements you want to.
Some bones have three functions at the same time.
Example:
Ribs:
Shape the body.
Protect the heart and lungs.
Provide a base for several muscles of the thorax.
The components of skeletal.
Cartilage: is flexible and softer than the bone. There is cartilage on the end of the, long bones, in the ears, the nose and on the ribs.
Bones: are very hard and resistant. They are made up of the tissue, and minerals like calcium. The minerals make the bones hard.
Joints: the place where two bones meet is called joint. There are two types of joints:
Fixed joints: the bones connected by fixed joints do not move.
Example: there are fixed joints between the bones in the skull.
Movable joints: the bones connected by movable joints can move. The wirts the union of the to move.
If there weren’t any joints, the skeletal would be rigid.
Muscular system:
Muscles and resistant and elastic. They are involved in the movement.
There are three types of muscles in your body.
Skeletal muscles: work together with bones. They are responsible for voluntary movements like chewing and walking.
Smoth muscles: form part of the organs inside the human body. The make involuntary movements.
For example:
The muscles of the esophagus are smoth muscles.
Cardiac muscle: is in the heart. This type of muscle never stops. It continues moving our entire lives. Cardiac muscle pumps blood with this movement.
Muscles contract and relax to produce movement. When a muscle contract, it gets smaller and pulls on the bone it is attached to. When the muscle relaxes it goes back to its original size. The bone then returns to it’s to initial position.
Movement: bones and muscles have to work together so that we can move. Muscles move when the nervous system send then order to move.
The nervous system coordinates the movements of the body in the following way.
1. The different sense organs gather information from the world around us.
2. The information passes to the sensory nerve in the sense organ. This nerve carries the information to the brain. When the information reaches the brain, we become aware of sounds, colors etc.
3. The brain interprets the information and orders a movement.
4. The motor nerves carry the brains orders to the muscles. When a muscle receives the order the move, it contracts. The muscle pull on the bone attached to, wich produces movement.
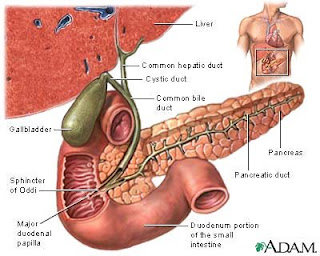
4.Asorpion:Asorpion takes place in the jejenum and the ileum of the small intestine during.Asorpion ,the nutrients formed during digestion pass into the bloodstream.
 miércoles, 28 de octubre de 2009
miércoles, 28 de octubre de 2009


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)